Embark on a mathematical journey as we unravel the sine definition, a fundamental concept in trigonometry that governs the cyclical nature of waves and oscillations. From its mathematical representation to its diverse applications, delve into the fascinating world of sine, where patterns and rhythms intertwine.
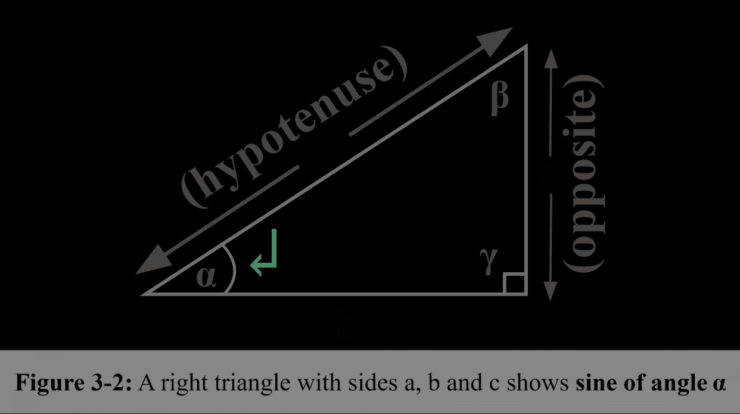
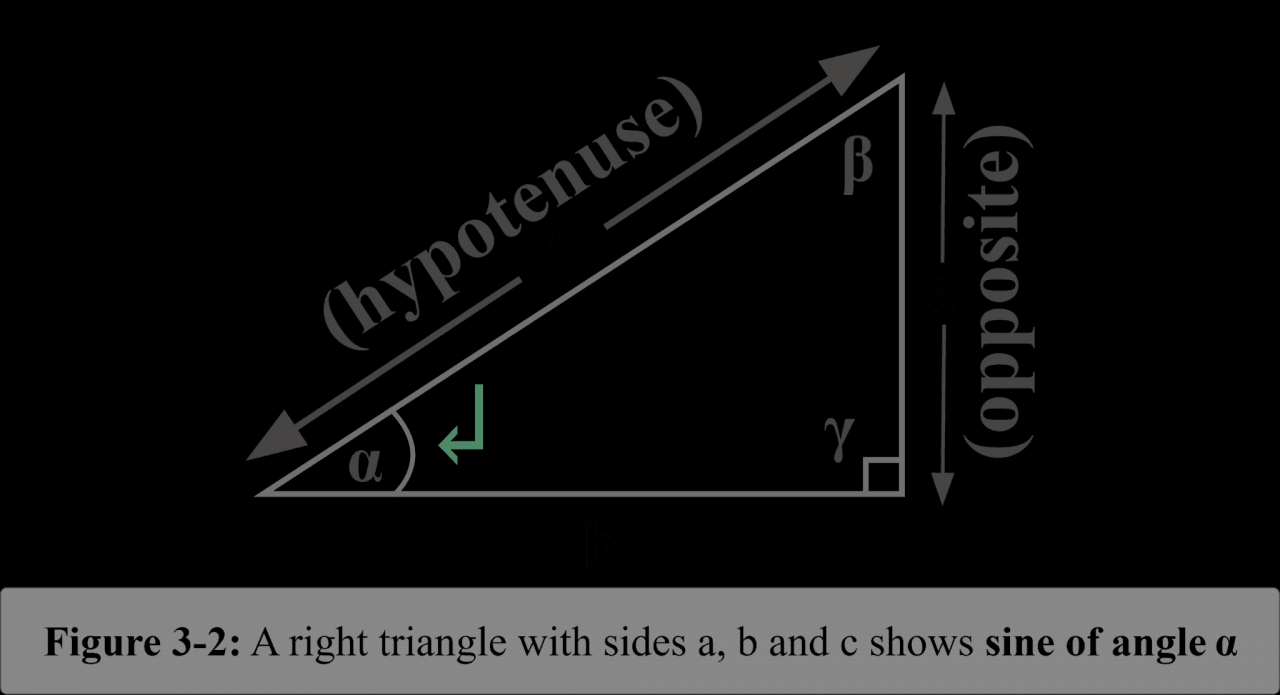
The sine function, denoted as sin(x), is a periodic function that oscillates between -1 and 1. It is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle, where x represents the angle measured from the horizontal.
Sine Definition
The sine function is a trigonometric function that describes the vertical displacement of a point on a unit circle as an angle is measured from the positive x-axis.
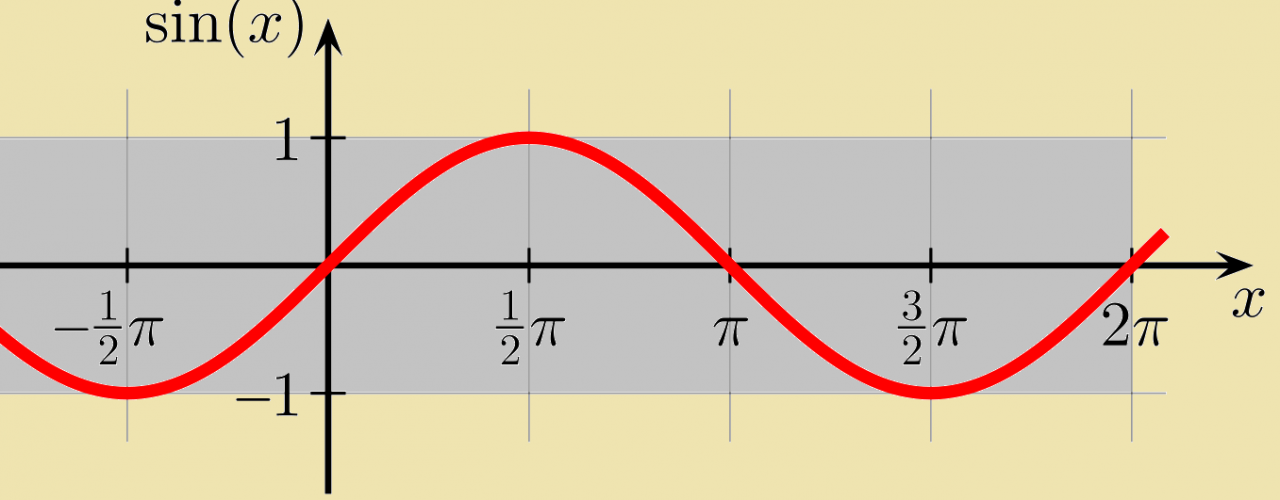
The sine wave is a periodic function that oscillates between -1 and 1. The period of a sine wave is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs, and the frequency is the number of cycles per second.
The mathematical definition of sine is:
sin(θ) = y/r
where θ is the angle, y is the vertical displacement, and r is the radius of the unit circle.
Sine waves are found in many real-world applications, including sound waves, electrical signals, and ocean waves.
Properties of Sine
Sine waves are periodic, meaning that they repeat themselves at regular intervals. The period of a sine wave is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs.
The amplitude of a sine wave is the maximum displacement from the center line. The frequency of a sine wave is the number of cycles per second.
The properties of sine waves can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena, including the motion of a pendulum, the vibration of a guitar string, and the propagation of sound waves.
Applications of Sine
Sine waves are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Sound waves: The sound waves that we hear are sine waves. The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch, and the amplitude of a sound wave determines its loudness.
- Electrical engineering: Sine waves are used in electrical engineering to generate alternating current (AC) power. AC power is used in many applications, including powering homes and businesses.
- Physics: Sine waves are used in physics to describe a wide variety of phenomena, including the motion of a pendulum, the vibration of a guitar string, and the propagation of sound waves.
Representing Sine
Sine can be represented in a variety of ways, including:
- Graphical representation: Sine can be represented graphically as a wave that oscillates between -1 and 1.
- Trigonometric representation: Sine can be represented trigonometrically as sin(θ), where θ is the angle.
- Exponential representation: Sine can be represented exponentially as e^(iθ), where i is the imaginary unit.
Each of these representations has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Related Concepts, Sine definition
Sine is closely related to a number of other mathematical concepts, including:
- Cosine: Cosine is another trigonometric function that is closely related to sine. Cosine is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
- Inverse sine: The inverse sine function is the function that gives the angle whose sine is a given value.
- Harmonic motion: Harmonic motion is a type of periodic motion that is described by a sine or cosine function.
Closing Summary: Sine Definition
In essence, the sine definition provides a powerful tool for understanding and analyzing periodic phenomena across various disciplines, from physics and engineering to music and signal processing. Its ability to model oscillations and waves makes it an indispensable concept in our exploration of the natural world.
FAQ Insights
What is the range of the sine function?
The range of the sine function is between -1 and 1.
What is the period of the sine function?
The period of the sine function is 2π.
What is the amplitude of the sine function?
The amplitude of the sine function is the maximum value of the function.